Settings
Consistent Hashing Ring is a special hashing algorithm primarily used for data distribution and load balancing in distributed systems. It maps the hash value space onto a ring structure, ranging from 0 to 2^32-1. This approach allows us to better handle node addition and removal while minimizing data migration.
Basic Principles of Consistent Hashing Ring
The core concept of consistent hashing ring is to visualize the entire hash value space as a circular structure with its ends connected, ranging from 0 to 2^32-1. In this circular space, we first need to distribute server nodes around the ring. Each server node is assigned a position on the ring through a hash function that calculates its hash value.
When we need to store or retrieve data, we use the same hash function to calculate the data's hash value to determine its position on the ring. After determining the data's position, we move clockwise along the ring until we encounter the first server node, which becomes the storage location for that data. This mechanism ensures a stable and predictable mapping relationship between data and servers.
The elegance of this design lies in its handling of server node changes. When adding or removing server nodes, only the data distribution between adjacent nodes is affected, avoiding global data redistribution. This significantly reduces data migration costs during system scaling or node failures.
Why Virtual Nodes?
In practical applications, the basic hash ring has a notable issue: when there are few server nodes, data distribution can become highly uneven. This occurs because hash function results may not be uniformly distributed around the ring, causing some server nodes to handle more data while others remain relatively idle. This data skew seriously affects system performance and availability.
As shown in the figure below, with only 10 physical nodes and no virtual nodes, we can clearly observe the uneven data distribution. Each ring segment represents a node's data range, and different colored nodes show significantly different data proportions. For example, the green node handles 176 keys while the orange node has no data, creating a huge disparity that leads to overload on the green node while the orange node's resources remain idle, resulting in inefficient system resource utilization.
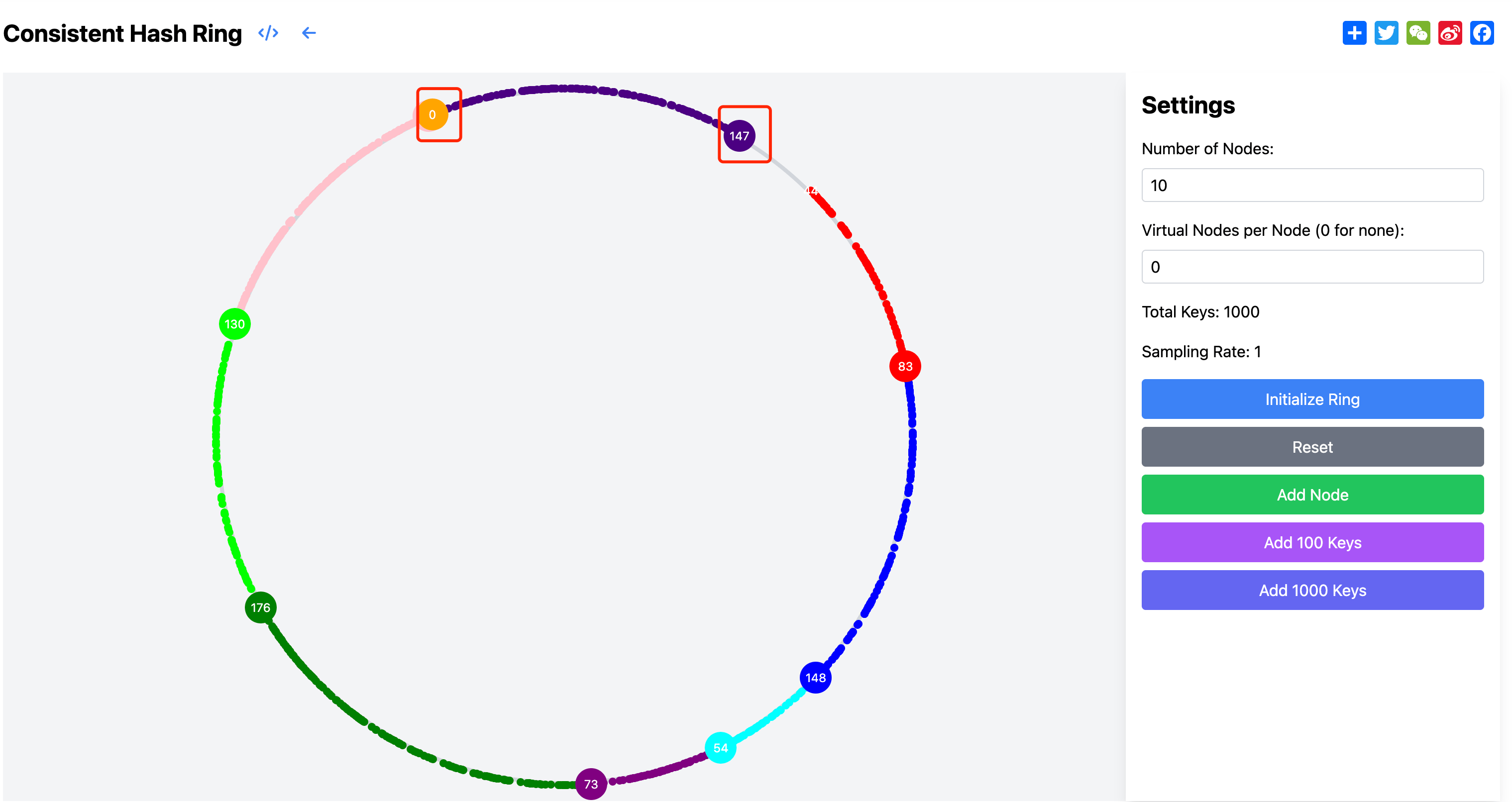
The root cause of this uneven distribution is that with fewer nodes, hash function results may not be evenly distributed around the ring, leading to larger gaps between some nodes and smaller gaps between others. Larger gaps mean that node must handle a larger data range and thus more requests. This problem is solved by introducing virtual nodes.
How Virtual Nodes Work
The core idea of virtual nodes is to virtualize each physical node into multiple virtual nodes. Specifically, the system creates multiple virtual replicas for each actual server node, with each virtual replica occupying a position on the hash ring. While these virtual nodes occupy different positions on the ring, they all ultimately map to the same physical server.
By introducing virtual nodes, we significantly increase the number of nodes on the ring, resulting in more uniform data distribution. For example, if we create 100 virtual nodes for each physical node, with just 4 physical nodes, we effectively have 400 distribution points on the ring. This approach effectively balances data load and reduces the risk of data skew. Additionally, the number of virtual nodes can be adjusted based on actual needs, providing more flexible load balancing capabilities.
Visualizing the Consistent Hashing Ring
In our interactive visualization tool, you can perform various operations to deeply understand the principles of consistent hashing ring and its data distribution characteristics.
Node Management Operations
You can observe how the consistent hashing ring dynamically adjusts data distribution through adding and removing nodes. Click the "Add Node" button on the interface to automatically add a new server node at a random position on the ring. Each node has a unique identifier and corresponding color marking for easy observation and distinction.
When you need to remove a node, simply click on that node and then click the delete button in the popup dialog. This process visually demonstrates how data is redistributed and why the consistent hashing algorithm minimizes data migration when nodes change.
Virtual Node Configuration
Virtual nodes are key to improving data distribution uniformity. On the interface, you can adjust the number of virtual nodes for each physical node. By default, each physical node has no virtual nodes, and you can set this value to observe its impact. When you adjust the number of virtual nodes, you can observe real-time changes in node distribution on the ring and how these changes affect data allocation.
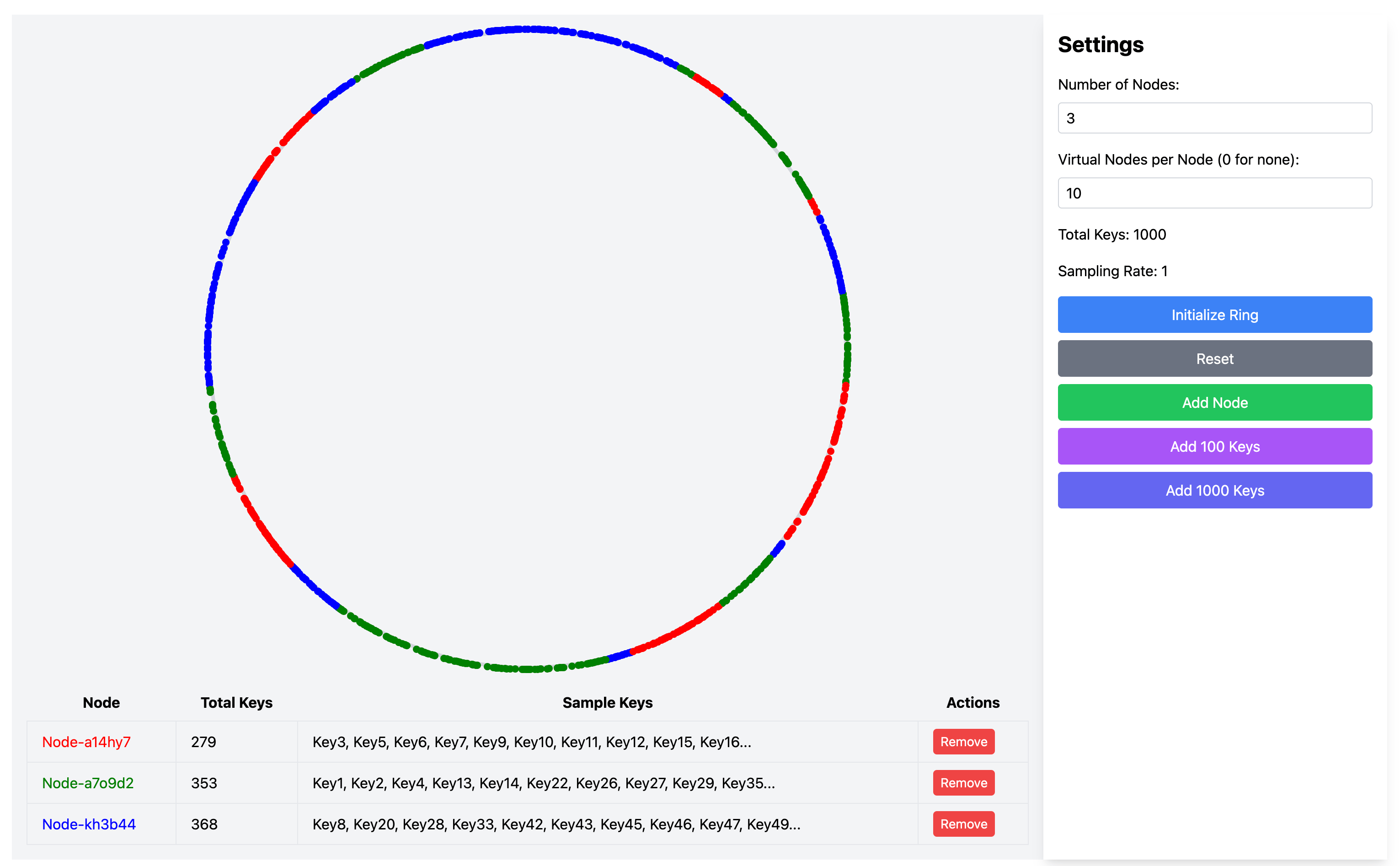
In the visualization interface, each virtual node appears as a small dot on the ring and is identified by the same color as its physical node. For example, if you set the number of virtual nodes to 10, each physical node will generate 10 virtual nodes on the ring, evenly distributed at different positions. When data needs to be stored, the system first finds the next node (which might be a virtual node) from the data's position, then stores the data on the physical node that the virtual node maps to.
By adding virtual nodes, we can clearly observe the data distribution becoming more uniform. Without virtual nodes, some physical nodes might be overloaded, but after adding virtual nodes, the load across physical nodes tends to balance. As shown in the figure below, by adjusting the number of virtual nodes, the previously uneven data distribution (where some nodes had significantly higher proportions) becomes more balanced, with data proportions becoming more consistent across physical nodes.
Real-time Feedback
All operations receive real-time visual feedback. When you add or remove nodes or adjust virtual node counts, you can observe:
- Real-time changes in data distribution proportions
- Dynamic adjustments of node responsibility ranges
- Distribution of virtual nodes on the ring
- Data migration processes and impact ranges
Through these interactive operations and visualization effects, you can better understand how the consistent hashing ring works and how virtual nodes help improve data distribution. We recommend trying different configuration combinations and observing system behavior changes to gain a deeper understanding of this important distributed system concept.
Advantages of Consistent Hashing Ring
The most significant advantage of consistent hashing ring is its excellent scalability. The system can dynamically add or remove nodes based on needs without causing large-scale data migration. When adding or removing nodes, only data between adjacent nodes needs redistribution, greatly reducing the overhead during system scaling. This feature allows the system to flexibly handle load changes and easily achieve horizontal scaling.
In terms of load balancing, consistent hashing ring achieves more uniform data distribution through virtual node technology. Each physical node can have multiple virtual nodes on the ring, significantly reducing the risk of data skew. Even when some areas have intensive data access, proper configuration of virtual node counts can ensure relatively balanced load distribution across physical nodes.
Furthermore, consistent hashing ring offers high availability. When a node fails, only the data handled by that node needs redistribution to other nodes, without affecting overall system operation. The system can quickly recover from failures by redistributing affected data to other nodes on the ring, ensuring service continuity.
Disadvantages of Consistent Hashing Ring
However, consistent hashing ring has some limitations. First, data distribution uniformity heavily depends on the chosen hash function. If the hash function quality is poor, it may lead to uneven data distribution on the ring, affecting load balancing. Therefore, in practical applications, careful selection of appropriate hash functions is necessary, often requiring a balance between performance and uniformity.
While the virtual node mechanism improves data distribution, it also increases system complexity. The system needs to maintain mapping relationships between many virtual nodes and actual physical nodes, which not only increases memory overhead but also affects lookup efficiency. In large-scale distributed systems, this additional overhead needs careful consideration during system design.
Additionally, the initial node count setting is an important factor. When the system starts with too few nodes, even with virtual nodes, uneven data distribution may occur. This requires careful planning of initial node counts and development of appropriate scaling strategies during system deployment.
Applications of Consistent Hashing Ring
Consistent hashing ring has wide applications in distributed systems. In distributed cache systems like Memcached, it's used to determine which node should store cache data. Through consistent hashing ring, the system can efficiently locate data positions and minimize data migration when nodes change.
In distributed storage systems, consistent hashing ring is used for data sharding and load balancing. It ensures data is evenly distributed across storage nodes while maintaining system stability during node scaling or failures.
For load balancers, consistent hashing ring provides an effective request distribution mechanism. It can distribute traffic evenly to different backend servers based on request characteristics, and when server counts change, only a small portion of requests need redistribution.
In distributed database systems, consistent hashing ring is commonly used for implementing data sharding strategies. It helps database systems distribute data evenly across multiple shards and minimizes data migration impact when shard counts change.